Minimally invasive surgery (MIS) has transformed modern healthcare by offering safer, more efficient alternatives to traditional open surgery. Using specialized tools, small incisions, and advanced imaging, MIS reduces trauma to the body, allowing for quicker recoveries and fewer complications. This article explores the benefits, common procedures, and recovery expectations associated with minimally invasive surgery.
Benefits of Minimally Invasive Surgery

Minimally invasive surgery offers significant advantages compared to traditional open surgery:
- Smaller Incisions: MIS uses tiny incisions, leading to minimal scarring and reduced risk of infection.
- Less Pain and Discomfort: Patients experience less postoperative pain, decreasing the need for strong pain medications.
- Quicker Recovery: Recovery times are shorter, allowing patients to return to daily activities faster.
- Reduced Hospital Stay: MIS often requires shorter hospital stays, reducing overall healthcare costs.
- Lower Risk of Complications: Smaller incisions and precise techniques result in a reduced risk of bleeding and infection.
These benefits make MIS a popular option for a wide range of procedures, improving patient outcomes and satisfaction.
Common Minimally Invasive Procedures
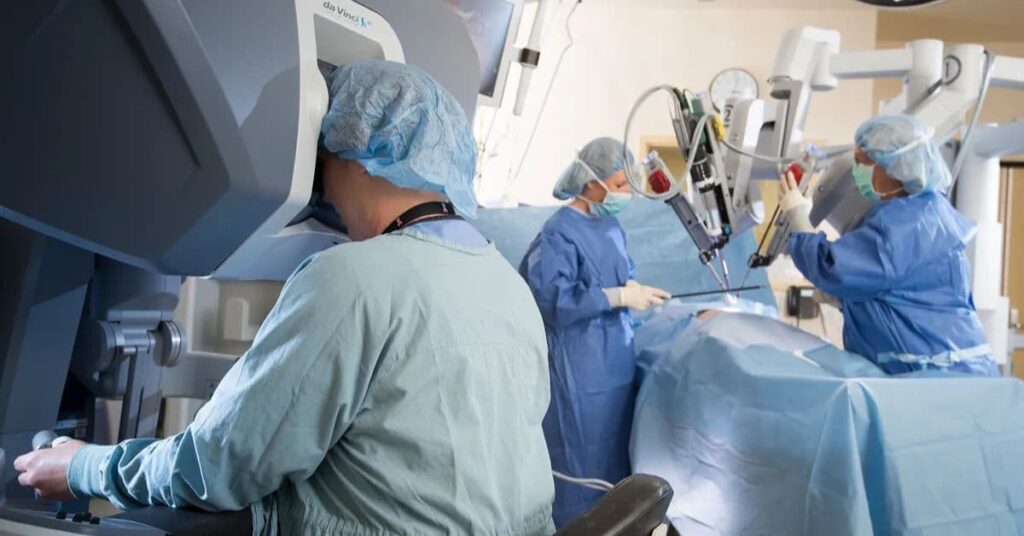
Minimally invasive techniques are used across various specialties, from general surgery to orthopedics and gynecology. Some common procedures include:
- Laparoscopic Surgery: Used for abdominal surgeries, such as gallbladder removal, hernia repairs, and appendectomies.
- Arthroscopy: Primarily used in orthopedic surgery to diagnose and treat joint issues, including knee and shoulder repairs.
- Endoscopic Procedures: Often used in gastroenterology to examine and treat digestive tract issues without incisions.
- Robotic-Assisted Surgery: Advanced robotic systems, like the Da Vinci robot, assist in complex surgeries with high precision, commonly used in prostatectomies and hysterectomies.
- Thoracoscopy: Used in thoracic surgery to access the lungs and chest cavity for lung biopsies or resections.
These procedures are often performed using a combination of cameras and tiny instruments that allow surgeons to operate with precision through minimal access points.
Recovery After Minimally Invasive Surgery
Recovery from MIS is typically faster and less intensive than recovery from traditional open surgery:
- Shorter Hospital Stays: Many patients are discharged the same day or within 1-2 days, depending on the procedure.
- Less Postoperative Pain: MIS patients generally experience less pain, leading to a reduced need for pain medication.
- Quicker Return to Activities: Patients can often resume light activities within days and return to regular activities within a few weeks.
- Fewer Restrictions: Unlike traditional surgery, MIS patients have fewer physical restrictions, making recovery smoother.
Patients are encouraged to follow their doctor’s instructions, attend follow-up appointments, and gradually resume physical activities to support healing.
Minimally invasive surgery offers patients numerous benefits, including reduced pain, faster recovery, and smaller scars. With applications across various medical fields, MIS has become an essential part of modern healthcare, enhancing patient outcomes and quality of life. As technology continues to advance, minimally invasive surgery is likely to become even more precise and accessible, making it the preferred choice for many surgical procedures.
