Surgery has evolved tremendously over centuries, from ancient, rudimentary practices to the highly advanced, minimally invasive techniques of today. This journey reflects the progress of human understanding of anatomy, medical innovations, and technological advancements. This article explores the fascinating history of surgery, highlighting key developments that have shaped modern surgical practices.
Ancient Beginnings of Surgery
The earliest forms of surgery date back thousands of years, with evidence of trepanation (drilling holes in the skull) found in ancient civilizations like Egypt, India, and Mesopotamia. Early surgeons used crude tools, such as sharp stones and bronze knives, to perform basic procedures, often with limited understanding and high risk. These practices were often combined with spiritual beliefs, as surgery was considered an attempt to release evil spirits or cure ailments.
Notable Ancient Practices
- Egyptian Surgery: Papyrus records indicate Egyptians performed wound treatments and amputations.
- Indian Surgery: Sushruta, an ancient Indian physician, is known for early surgical texts describing skin grafts and cataract surgeries.
Middle Ages and Renaissance: Advancements and Challenges
During the Middle Ages, surgery was generally seen as a last resort. Religious prohibitions and limited anatomical knowledge hindered progress. However, the Renaissance sparked renewed interest in human anatomy, allowing surgeons to explore more effective techniques.
- Anatomical Studies: Leonardo da Vinci’s detailed drawings and Andreas Vesalius’ anatomical texts laid foundations for modern surgical anatomy.
- Battlefield Surgery: Military conflicts spurred advances, with surgeons treating injuries and amputations on the battlefield.
19th Century: Breakthroughs in Anesthesia and Sterilization
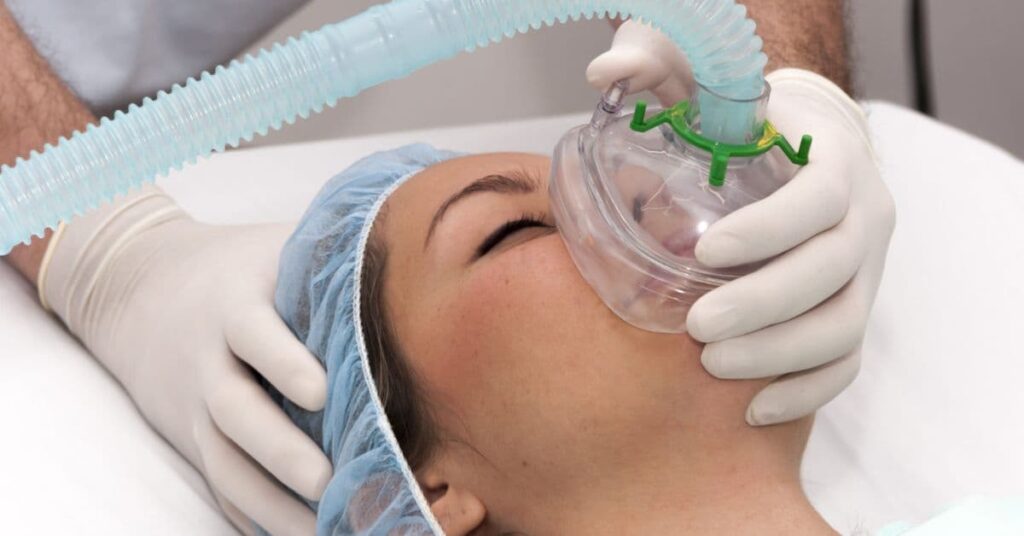
The 19th century brought two revolutionary changes that transformed surgery: anesthesia and antiseptics. These developments reduced pain and infection risk, making surgery safer and more accessible.
- Anesthesia (1846): The discovery of ether and chloroform allowed for pain-free surgeries.
- Antiseptics (1867): Joseph Lister’s introduction of antiseptics in surgery reduced infection rates and set standards for hygiene in operating rooms.
20th Century: Rise of Modern Surgical Techniques
The 20th century saw incredible advancements, such as open-heart surgery, organ transplants, and minimally invasive techniques, revolutionizing patient outcomes.
- Organ Transplants: In the 1950s, the first successful kidney transplant paved the way for heart, liver, and lung transplants.
- Laparoscopic Surgery: Minimally invasive techniques, introduced in the 1980s, reduced recovery times, pain, and scarring.
21st Century: Robotic and Precision Surgery
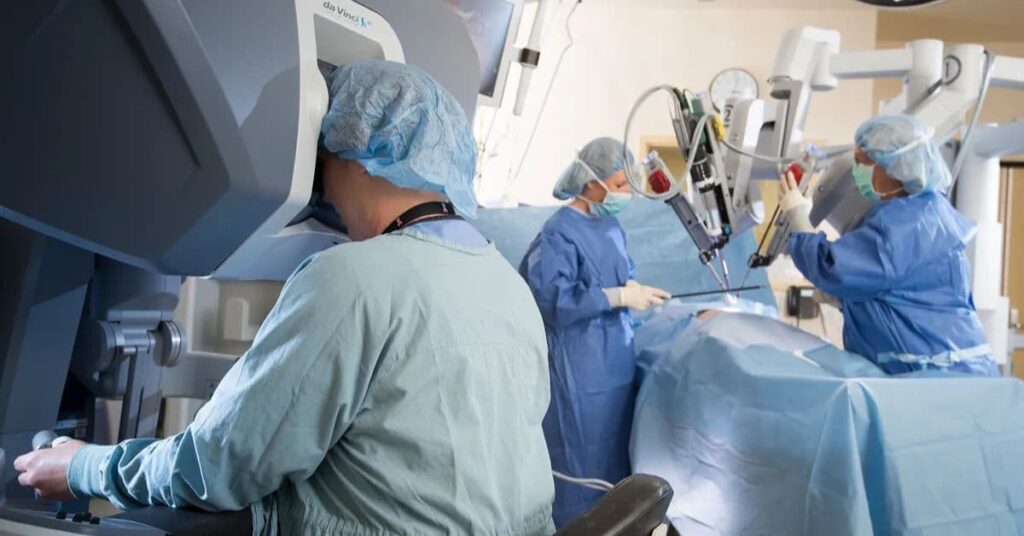
Today, surgery is becoming more precise and less invasive than ever, thanks to robotics, AI, and advanced imaging technologies.
- Robotic-Assisted Surgery: Systems like the Da Vinci robot enable surgeons to perform complex procedures with greater accuracy.
- 3D Printing and Bioprinting: These technologies are creating custom implants and potentially regenerating tissues, promising transformative changes in reconstructive surgery.
The evolution of surgery from ancient techniques to modern, minimally invasive methods reflects humanity’s resilience and commitment to improving patient care. With advancements like robotics, AI, and regenerative medicine, the future of surgery holds immense potential for personalized and precise treatments, continuing the legacy of innovation that defines this field.
