The gut microbiome, a complex community of trillions of microorganisms residing in our digestive system, plays a vital role in supporting overall health and immune system function. These beneficial bacteria, viruses, and fungi interact closely with immune cells, helping the body respond to pathogens, regulate inflammation, and maintain a balanced immune response. This article explores the connection between the gut microbiome and the immune system and highlights ways to support a healthy gut for optimal immune function.
Understanding the Gut Microbiome
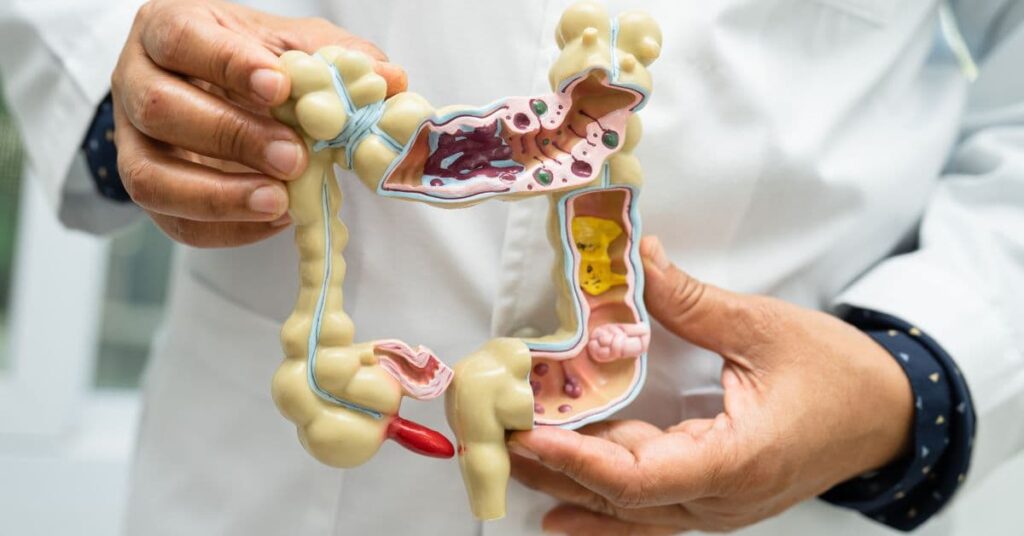
The gut microbiome consists of diverse microorganisms that coexist in the digestive tract. These microbes support digestion, produce vitamins, and play a crucial role in immune health by interacting with the body’s immune cells and influencing immune responses. A balanced microbiome, with beneficial bacteria in healthy proportions, is essential for a well-functioning immune system, while imbalances can lead to weakened immunity and increased inflammation.
How the Gut Microbiome Supports Immune Health
The gut microbiome and immune system communicate closely, with beneficial microbes stimulating immune cells to create a balanced, responsive defense. Here are key ways the microbiome impacts immune health:
- Training Immune Cells: Beneficial bacteria help “train” immune cells, teaching them to differentiate between harmful invaders and harmless substances, reducing the risk of autoimmune reactions.
- Regulating Inflammation: The gut microbiome produces short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate, which reduce inflammation and support immune regulation.
- Strengthening the Gut Barrier: A healthy microbiome enhances the intestinal barrier, preventing pathogens from entering the bloodstream and triggering an immune response.
- Promoting Immune Tolerance: The gut microbiome helps maintain immune tolerance, lowering the risk of allergies and immune-related diseases.
Signs of an Imbalanced Gut Microbiome
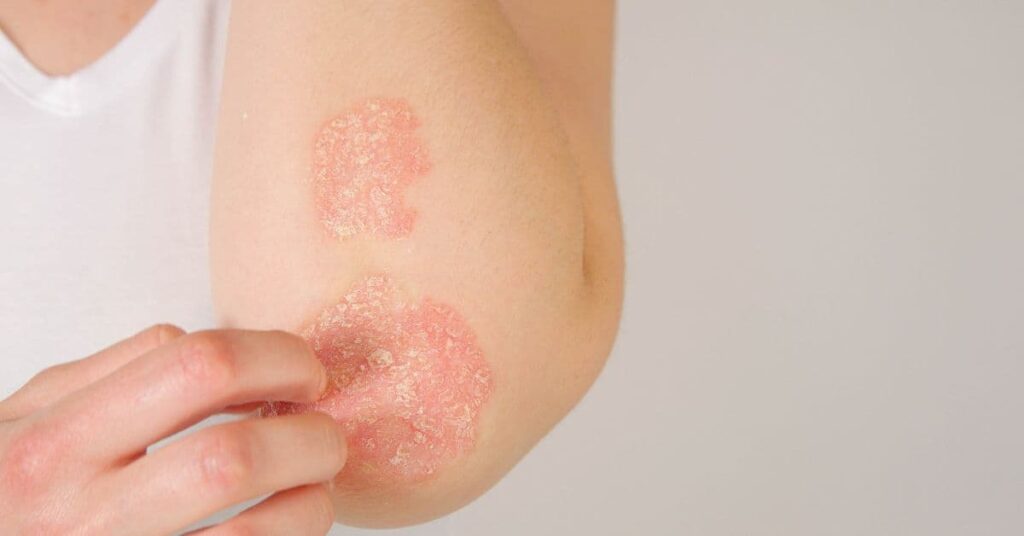
An imbalance in the gut microbiome, known as dysbiosis, can affect immune function and overall health. Common signs of dysbiosis include:
- Digestive issues like bloating, gas, or irregular bowel movements.
- Frequent infections or weakened immunity.
- Skin problems, such as eczema or acne.
- Food intolerances or allergies.
Supporting a Healthy Gut Microbiome for Immune Health
Maintaining a balanced gut microbiome is essential for optimal immune function. Here are some strategies to support gut health:
1. Eat a Diverse Diet
A diet rich in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides fuel for beneficial bacteria and promotes microbial diversity, which is linked to stronger immunity.
2. Include Probiotic and Prebiotic Foods
- Probiotics: Fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi introduce beneficial bacteria into the gut.
- Prebiotics: Foods like garlic, onions, bananas, and asparagus contain fibers that feed healthy bacteria.
3. Limit Processed Foods and Sugars
Highly processed foods and added sugars can promote the growth of harmful bacteria, disrupting the microbiome balance and weakening immunity.
4. Stay Hydrated
Water is essential for digestion and helps support the movement of beneficial bacteria through the digestive system.
5. Manage Stress
Chronic stress can negatively impact the gut microbiome and immune function. Practices like meditation, exercise, and deep breathing can help maintain balance.
6. Use Antibiotics Responsibly
Antibiotics disrupt the microbiome by killing both harmful and beneficial bacteria. Use antibiotics only when necessary and follow up with probiotics to support microbiome recovery.
The gut microbiome plays a critical role in immune system function, helping to regulate inflammation, support immune cell training, and maintain the gut barrier. By adopting healthy habits like a balanced diet, reducing stress, and including probiotics and prebiotics, you can promote a balanced gut microbiome that strengthens immune health. Maintaining a healthy microbiome is an essential part of a robust immune system and a foundation for overall well-being.
