Hyperpigmentation is a common skin condition characterized by darkened patches or spots on the skin. It occurs when excess melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color, accumulates in certain areas. While hyperpigmentation is usually harmless, it can affect self-confidence and appearance. In this article, we’ll explore the causes, treatments, and prevention strategies to help you manage and prevent hyperpigmentation effectively.
What Causes Hyperpigmentation?

Hyperpigmentation can be triggered by several factors, including:
- Sun Exposure: UV rays stimulate melanin production, leading to sunspots or age spots.
- Hormonal Changes: Conditions like pregnancy or the use of birth control pills can trigger melasma, a type of hyperpigmentation.
- Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH): This occurs after skin injuries or inflammatory conditions like acne, eczema, or cuts.
- Medication Side Effects: Certain medications, such as chemotherapy drugs, can cause skin discoloration.
- Skin Aging: As skin ages, it becomes more prone to dark spots and uneven pigmentation.
Types of Hyperpigmentation
- Melasma: Appears as brown or gray patches, often on the face, and is commonly triggered by hormonal fluctuations.
- Sunspots (Lentigines): Flat, brown spots that develop due to prolonged sun exposure, usually on sun-exposed areas like the face and hands.
- Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH): Dark spots that form after an injury or inflammation heals, such as acne scars or eczema.
Effective Treatments for Hyperpigmentation
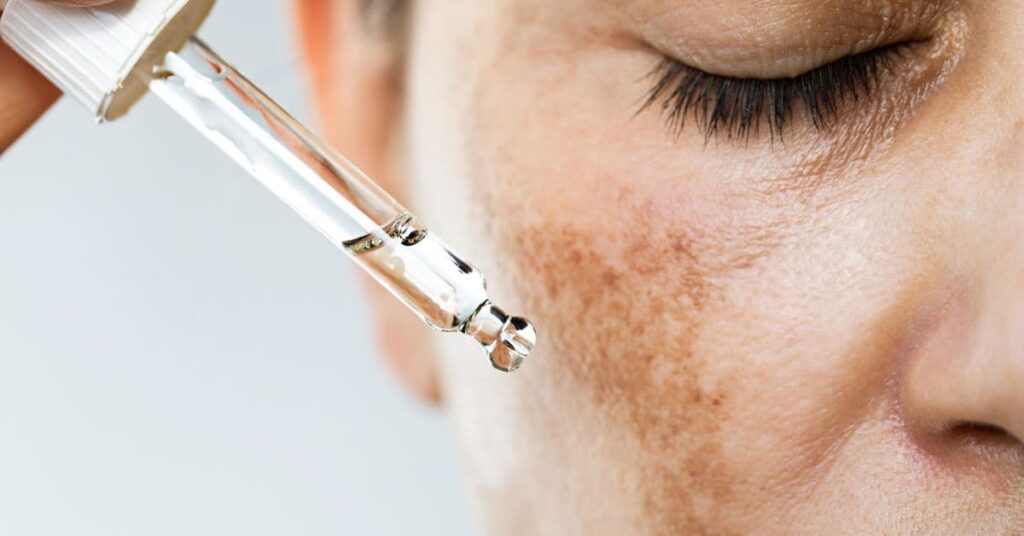
1. Topical Treatments
- Hydroquinone: A powerful skin-lightening agent that reduces melanin production.
- Retinoids: Stimulate cell turnover, helping fade dark spots over time.
- Vitamin C: An antioxidant that brightens skin and reduces pigmentation by inhibiting melanin production.
- Azelaic Acid: Effective for both acne and hyperpigmentation by preventing melanin synthesis.
2. Chemical Peels
Chemical peels use acids like glycolic acid or salicylic acid to exfoliate the skin and reduce pigmentation. They promote the growth of new, evenly pigmented skin cells.
3. Laser Treatments
Lasers, such as Q-switched or fractional lasers, target and break down excess melanin. These treatments are effective for more severe cases of hyperpigmentation.
4. Microdermabrasion and Microneedling
Both procedures stimulate collagen production and improve skin texture while helping to fade dark spots over time.
Prevention Tips for Hyperpigmentation
- Use Sunscreen Daily: Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher every day, even on cloudy days.
- Avoid Peak Sun Hours: Minimize sun exposure between 10 AM and 4 PM, when UV rays are strongest.
- Wear Protective Clothing: Hats, sunglasses, and long sleeves can help protect your skin from sun damage.
- Treat Skin Gently: Avoid picking or squeezing pimples, which can lead to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
- Choose Non-Irritating Products: Use skincare products suited to your skin type to prevent irritation and inflammation.
When to See a Dermatologist
If hyperpigmentation persists or worsens despite home treatments, consulting a dermatologist is recommended. They can offer tailored treatments, such as prescription-strength topical solutions or advanced laser therapies, to address more severe pigmentation issues.
Hyperpigmentation is a common yet manageable skin concern. Understanding its causes and using targeted treatments can help reduce the appearance of dark spots and restore an even skin tone. Prevention plays a crucial role, with sun protection being one of the most effective strategies. With consistent care and, if necessary, professional help, it’s possible to manage hyperpigmentation and achieve healthier, more radiant skin.
