Eczema and psoriasis are two of the most common chronic skin conditions, often causing confusion because of their similar symptoms. However, they differ in terms of causes, triggers, and treatments. Both conditions can have a significant impact on quality of life, leading to discomfort, inflammation, and emotional stress. This article explores the key differences between eczema and psoriasis, common symptoms, and effective treatment options for each.
1. What is Eczema?
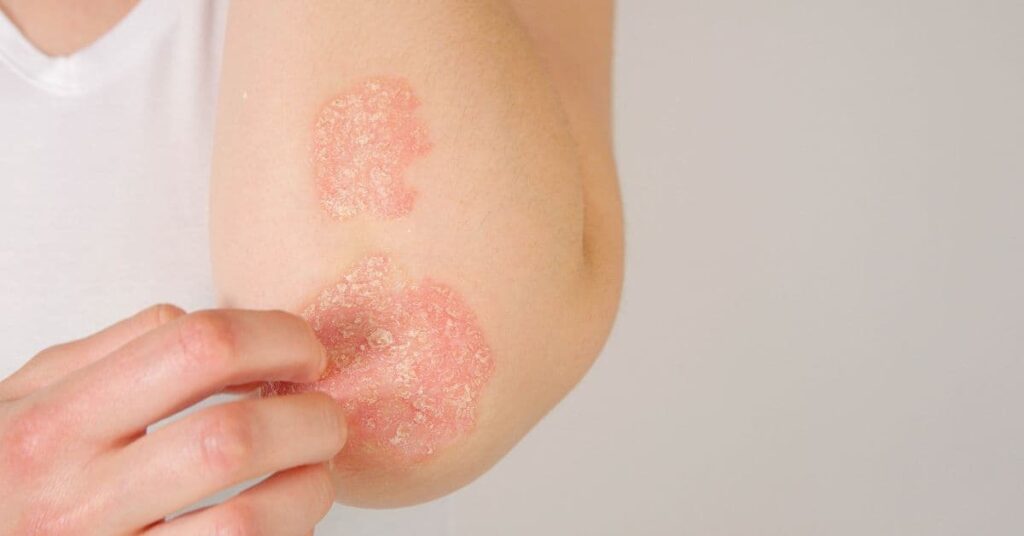
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition. It often begins in early childhood and may persist or recur throughout life. Eczema is linked to a combination of genetic and environmental factors, including an overactive immune response to allergens or irritants. Common triggers include harsh soaps, allergens, weather changes, and stress.
Symptoms of Eczema
- Dry, itchy skin that may become red and inflamed.
- Fluid-filled blisters that ooze or crust over.
- Thickened, scaly patches from frequent scratching.
- Often found in areas like the inside of elbows, behind knees, and around the neck.
- Symptoms tend to flare up and subside periodically.
2. What is Psoriasis?
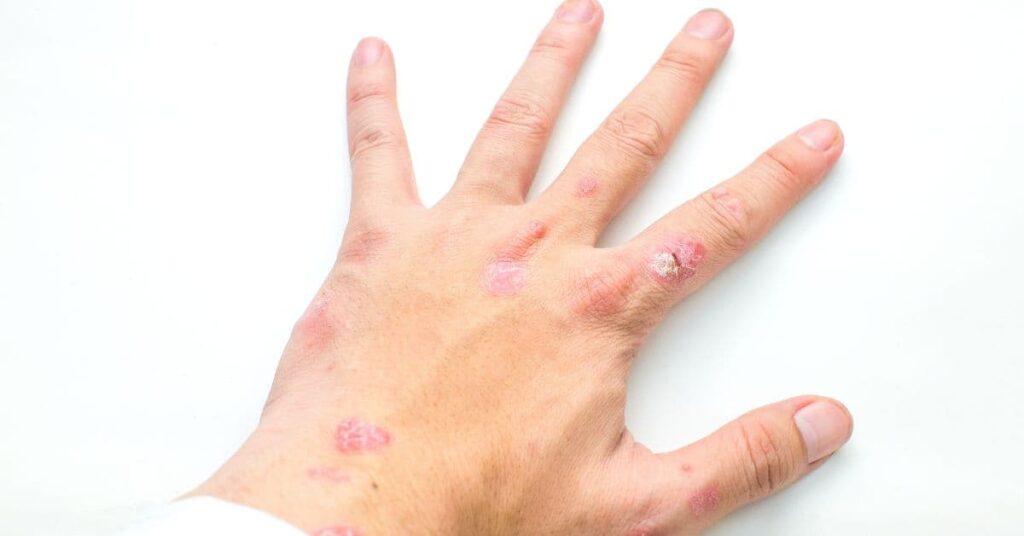
Psoriasis is an autoimmune condition that speeds up the life cycle of skin cells, causing a buildup of cells on the surface of the skin. This results in thick, scaly patches called plaques. Psoriasis tends to be more persistent than eczema and can be linked to genetic predisposition. Triggers include infections, stress, cold weather, and certain medications. Psoriasis also has systemic implications, sometimes associated with psoriatic arthritis, which affects the joints.
Symptoms of Psoriasis
- Raised, red patches covered with silvery-white scales.
- Itching or burning sensation on affected areas.
- Cracked, dry skin that may bleed.
- Most commonly affects the scalp, knees, elbows, and lower back.
- Psoriasis plaques tend to be more defined than eczema rashes.
3. Differences Between Eczema and Psoriasis
While both conditions cause red, itchy patches, there are some clear distinctions:
- Onset: Eczema often starts in childhood, while psoriasis can develop at any age but usually appears in adulthood.
- Triggers: Eczema is commonly triggered by environmental allergens, while psoriasis is linked to immune system dysfunction and genetics.
- Appearance: Psoriasis plaques are thicker and more defined, often with silvery scales, whereas eczema presents with dry, cracked skin and occasional weeping blisters.
- Location: Eczema usually appears in skin folds (e.g., elbows and knees), while psoriasis commonly affects the scalp, knees, and elbows.
4. Treatment Options for Eczema and Psoriasis
Eczema Treatment
Managing eczema involves reducing inflammation and keeping the skin hydrated:
- Moisturizers and Emollients: Apply daily to prevent dryness and restore the skin barrier.
- Topical Corticosteroids: Used during flare-ups to control inflammation and itching.
- Antihistamines: Help relieve itching and improve sleep.
- Lifestyle Changes: Avoid known triggers, such as allergens, stress, and harsh chemicals.
- Immunomodulators: For severe cases, topical or oral medications can reduce immune system overactivity.
Psoriasis Treatment
Psoriasis treatment aims to slow down the production of skin cells and reduce inflammation:
- Topical Steroids and Vitamin D Analogues: Help reduce inflammation and slow skin cell turnover.
- Salicylic Acid and Coal Tar: Used to soften and remove scales.
- Phototherapy (UV Light Therapy): Reduces symptoms by slowing skin cell growth.
- Systemic Medications: In more severe cases, oral medications or biologic therapies (such as TNF inhibitors) may be prescribed to target the immune system.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Managing stress, avoiding alcohol, and maintaining a healthy diet can help minimize flare-ups.
5. Living with Eczema and Psoriasis
Both eczema and psoriasis are chronic conditions that require ongoing management. Although there is no permanent cure for either, consistent treatment and lifestyle changes can significantly improve quality of life. Emotional support is also essential, as these conditions can impact self-esteem and mental health. Joining support groups or consulting a dermatologist can be helpful in managing both physical and emotional aspects of these skin disorders.
Eczema and psoriasis may have overlapping symptoms, but they are distinct conditions with different causes, appearances, and treatment options. Eczema is typically associated with environmental triggers and allergies, while psoriasis is an autoimmune condition with genetic roots. Proper diagnosis and treatment are essential for managing these conditions effectively. With the right care and lifestyle adjustments, it’s possible to minimize flare-ups and maintain healthier skin. Consulting a dermatologist can help individuals develop a tailored treatment plan for long-term management.
